Process Management
All you need to know about process management
What is process management?
Before talking about process management, it is important to understand the concept of process. The company can be represented as a network of flows (processes) that cross it to bring a product or a service (value) to its customers.
The processes start from the needs and expectations of customers and run through the company while respecting quality, cost and deadline objectives. Therefore, process management is the ability of a company to ensure, through its processes, the efficiency and productivity of its organization for better profitability and greater customer satisfaction.
As a result, process management is a key subject for the company and its performance. Many methodologies and tools have been developed to optimize processes in order to support companies growth.
Methodologies to improve business processes
Kaizen could be translated as “continuous improvement”. This method aims to make small changes to the process every day. The constant search for solutions to the smallest problem makes change more accessible because it is done in small steps. More than a methodology, Kaizen has also become a state of mind in organizations using it.
The main principles :
- Constantly question yourself
- Do not aim for perfection but for continuous improvement
- Identify the original causes of problems
- Solve problems without delay
- Prioritize changes
- Involve everyone in the change
Advantage: sudden changes can run up against problems of change management and some people may be reluctant to change. Small, repeated changes accompany profound changes over time and are more easily accepted.
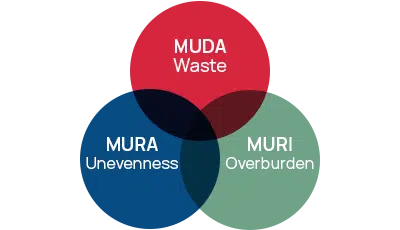
Lean management is a methodology that was formalized by American researchers at the Massachussets Institute of Technology (MIT). Lean Management” is an English expression whose term “lean” is evocative, it means “fat free” or “lean”. The very principles of this methodology are to eradicate the unnecessary and to focus on what brings value by applying the 3M hunt:
The first concerns the elimination of actions and activities in a process that do not bring value. The second is the elimination of unnecessary and counter-productive process variations. Finally, the last one eliminates the excesses: everything that induces constraints or unreasonable efforts of the employees or even of the company’s resources.
Advantage: reduce waste as much as possible and on all dimensions that impact the profitability of the company: time, material, money to increase performance and profitability.
The objective of this methodology is to deliver products or services that comply with the customer promise. Compliance will depend largely on the variability of the processes: once a process has been defined, the Six Sigma methodology ensures that the difference between the process operated and the target process does not exceed Six Sigma (or 6 times the standard deviation – Sigma in Greek).
Therefore, this methodology is applied to constantly measure the conformity of the processes operated in the field. The more homogeneous and similar they are, the more the customer promise will be respected and the product accepted by the final customer. It was originally applied in the industrial sector and then spread to all the company’s processes: administrative, R&D, sales, etc.
Advantage: the emphasis placed on the quality of the processes and therefore the quality of the products/services delivered. Customer satisfaction is mostly achieved because the promise is delivered.
Lean Six Sigma has naturally imposed itself by combining the best of the last two methodologies: fighting waste and achieving a high level of quality.
It is often deployed in project mode, respecting the following DMAIC phases:
In theory, there is no methodology specific to Lean SixSigma, but the two are used in a complementary manner: you decide to rationalize your manufacturing processes by applying Lean, which will cause changes and difficulties in your processes. Variations will then appear: you will use Six Sigma to resolve these new variations.
Advantage: really maximize the available resources (profitability) while delivering the customer promise (quality).
Kind of tools for process management
In addition to these methodologies, new digital tools have been added to the range of products available to further optimize process performance.
Process mapping tools allow you to easily create the flows and different steps of your processes. It also allows you to clearly identify the objective and responsibilities of each person at each step of the process.
The advantage of these solutions is that they allow you to quickly visualize your flows, to clearly define the objectives and to align the different departments of your organization around your transversal business processes.
BPM is a way to define and map the different steps of a process, taking into account the interactions between people, information systems and other elements that have an impact on the process. A phase of interview, audit and understanding of the globality of the process to be modeled is essential to have an exhaustive view. In the case of BPM use, it is frequent that the process is fixed and that the passage from one stage to another is strictly regulated, as can be the case in the process of obtaining a bank loan.
The interest of BPM is to be able to model and diagram (BPMN) all the flows and activities of the company. This global view is a first step towards the analysis and optimization of business processes. It is essential in certain sectors such as the banking sector in order to better manage its processes and prevent any anomaly or non-compliance.
These tools, as their name indicates, add a layer of intelligence to BPM tools. They can include process simulation modules to validate that a process change will improve performance, performance indicator modules for these processes, etc.
The main interest of these tools is to complete the initial offer and to gain in value on the management and optimization of business processes.
Process mining only collects data from information logs to reconstruct in real time how processes are operated in the field. Reliable, based on facts, and dynamic, based on flows and time space, process mining gives a clear and visual vision of possible process anomalies (rework, bottlenecks...). AI and ML (link article AI/ML) coupled with process mining will give valuable information on the optimization and automation of all or part of your processes. They will even allow you to project yourself into the future to better anticipate and make the right decisions today for tomorrow. Process mining is often appreciated as a complement to BPM because of its dynamic, analytical and predictive contribution to processes.
The gains are often financial and in customer satisfaction by allowing a significant improvement in productivity and process performance.